1.发错板块,下不为例。
2.C语言中规定char类型占一个字节,short类型占两个字节。如你所说A的ascii为65,那1的ascii为49,他们最后都是以ascii方式存储的。
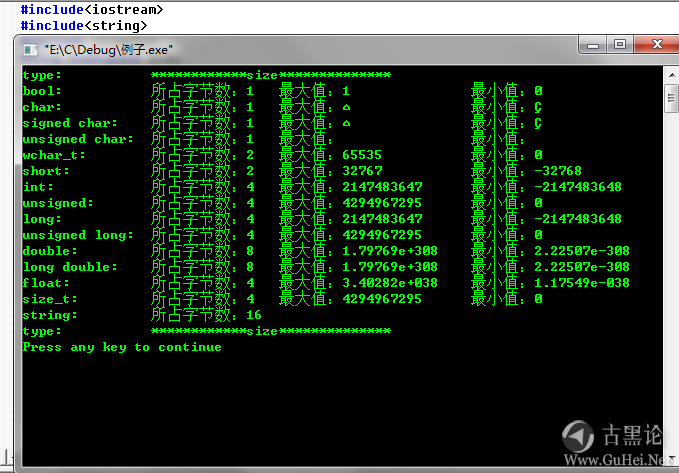
最后给上 int、long、double、char表示范围(最大最小值)
👀🏠🍭™🪰
全屏查看- #include<iostream>
- #include<string>
- #include <limits>
👍🏠🫑🅰🐴
- using namespace std;
-
- int main()
- {
- cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl;
🤙🌕🌶❎🐢 - cout << "bool: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(bool);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::max)();
- cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "char: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(char);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::max)(); 👳💎🪥😃🤳
- cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "signed char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(signed char);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::max)();
- cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "unsigned char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned char);
🙌🫖🚭🐻 - cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::max)();
- cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "wchar_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(wchar_t);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::max)();
- cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::min)() << endl; 🧑🍳🛍🎺☠👂
- cout << "short: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(short);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::max)();
- cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "int: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(int);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::max)(); 🧑💻🩳📮💀💅
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "unsigned: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::max)();
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "long: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long); 🧑🌾👞🩸🤛
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::max)();
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "unsigned long: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned long);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::max)();
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::min)() << endl;
👃🏠🥄🈷🦖
- cout << "double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(double);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::max)();
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "long double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long double);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::max)(); 👳🎩📡😷👌
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "float: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(float);
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::max)();
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "size_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(size_t);
🧑🌾👒🪝😈✋
- cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::max)();
- cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "string: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(string) << endl;
- // << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<string>::max)() << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<string>::min)() << endl;
- cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl; 🧑🍳👞🔭☠🙌
- return 0;
- }
🖕🚗🍒🅾🕊

 「初入古黑」
2016-9-16 01:37
「初入古黑」
2016-9-16 01:37
 变色卡
变色卡 古黑论管理员,在论坛上有什么问题都可以找他。
古黑论管理员,在论坛上有什么问题都可以找他。